-1-scaled.jpg)
_0-2-scaled.jpg)
_0-3.jpg)

_0-4-scaled.jpg)
_0-5-808x1024.jpg)
_0-6.jpg)
_0-7.jpg)
_0-7-副本.jpg)
_0-11-367x1024.jpg)
251210.jpg)
_0-9-762x1024.jpg)

_0-11-1024x187.png)
M-CHAT-R/F:
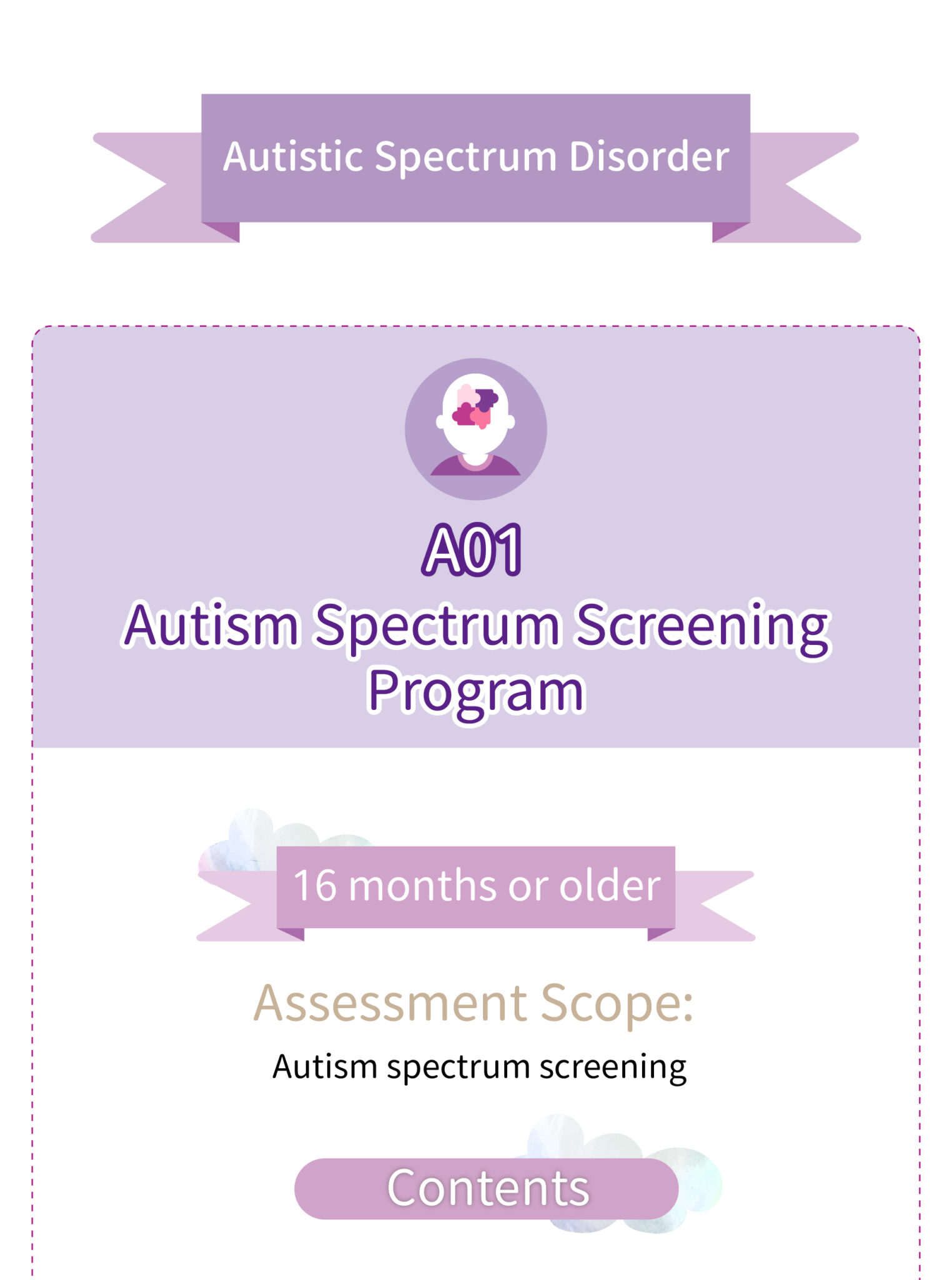
The M-CHAT-R/F (Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers, Revised) is the most recommended autism screening tool by the American Academy of Pediatrics as of 2019. It is designed to assess the risk of autism in preschool children aged 16 months and older by asking about 20 behaviors related to your child’s actions. The results will indicate whether further evaluation is needed and guide discussions with a pediatrician on the next steps for treatment.
Social Communication Questionnaire (SCQ):
The SCQ is a widely used screening tool in academic research for autism spectrum disorders. It consists of 40 questions for parents to answer, screening children with a chronological age over 4 years and a mental age over 2 years.
qEEG brainwave Analysis:
Using a device equipped with 19 sensors, the qEEG collects brainwave activity from different parts of the brain. The sensors, placed on the scalp, capture the brainwaves, which are then compared with a database to identify abnormalities. This helps pediatricians and psychiatrists effectively assess, screen, and provide further treatment for emotional problems and disorders in children.
_0-14.jpg)

_0-16-1024x187.png)
ADOS-2:
The Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Second Edition (ADOS-2), is an assessment tool used to diagnose and differentiate autism. A professional assessor observes the child’s behavior in a standardized setting using various tools and modules, suitable for children 12 months and older as well as adults. ADOS is regarded as the gold standard for autism diagnosis in many countries and is widely used worldwide.
qEEG Neurofeedback Analysis:
Using a device equipped with 19 sensors, the Neurofeedback collects brainwave activity from different parts of the brain. The sensors, placed on the scalp, capture the brainwaves, which are then compared with a database to identify abnormalities. This helps pediatricians and psychiatrists effectively assess, screen, and provide further treatment for emotional problems and disorders in children.
DSM-5:
Our pediatricians and psychiatrists use the DSM-5® (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition) published by the American Psychiatric Association as the standard for diagnosing various mental disorders. Mental disorders do not always fit neatly into a single disease category; DSM-5® provides clear classifications of distinct disorders. Some symptom areas, such as depression and anxiety, span multiple diagnostic categories and may reflect common underlying vulnerabilities across a broad range of disorders.
.jpg)
212121.png)
_0-21.png)
Strengthsthe and Normal Behaviour Scale (SWAN):
The SWAN is an internationally recognized tool supported by multiple medical studies for screening ADHD. It assesses 18 related characteristics to identify:
1.ADHD-Inattentive Type
2.ADHD-Hyperactive/Impulsive Type
3.Combined Type (Hyperactive and Inattentive)
Target Group:
Children aged 6-18 years (many medical studies also validate SWAN for children aged 4 and above)
qEEG Brainwave Analysis:
Using a device equipped with 19 sensors, the qEEG collects brainwave activity from different parts of the brain. The sensors, placed on the scalp, capture the brainwaves, which are then compared with a database to identify abnormalities. This helps pediatricians and psychiatrists effectively assess, screen, and provide further treatment for emotional problems and disorders in children.
24254_0-24.png)
24254_0-25.png)
_0-26.png)
Symptoms and Normal Behaviour Scale (SWAN): The SWAN is an internationally recognized tool supported by multiple medical studies for screening ADHD. It assesses 18 related characteristics to identify:
1. ADHD-Inattentive Type.
2. ADHD-Hyperactive/Impulsive Type.
3. Combined Type (Hyperactive and Inattentive). Target Group: Children aged 6-18 years (many medical studies also validate SWAN for children aged 4 and above)
qEEG Brainwave Analysis: Using a device equipped with 19 sensors, the qEEG collects brainwave activity from different parts of the brain. The sensors, placed on the scalp, capture the brainwaves, which are then compared with a database to identify abnormalities. This helps pediatricians and psychiatrists effectively assess, screen, and provide further treatment for emotional problems and disorders in children.
_0-29-scaled.jpg)
_0-30-scaled.jpg)
-6.png)
_0-32-scaled.jpg)
_0-33-scaled.jpg)
-4.png)
_0-35-scaled.jpg)
353535.png)
_0-37.jpg)
_0-38-scaled.jpg)
_0-39.jpg)
_0-40-scaled.jpg)
_0-41.jpg)
_0-42-scaled.jpg)
_0-43.jpg)
434343.png)
_0-45.jpg)
_0-46-scaled.jpg)
_0-47.png)
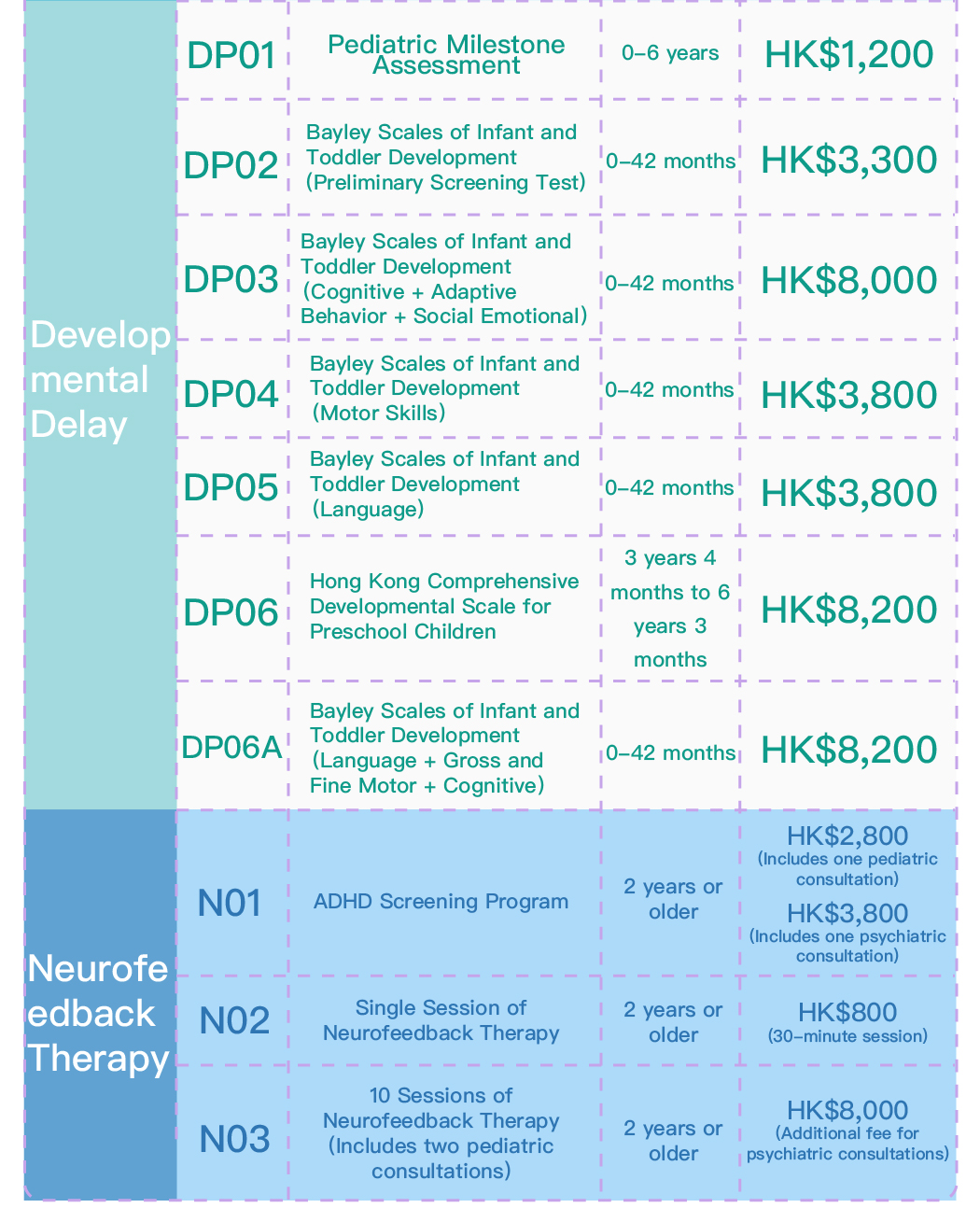
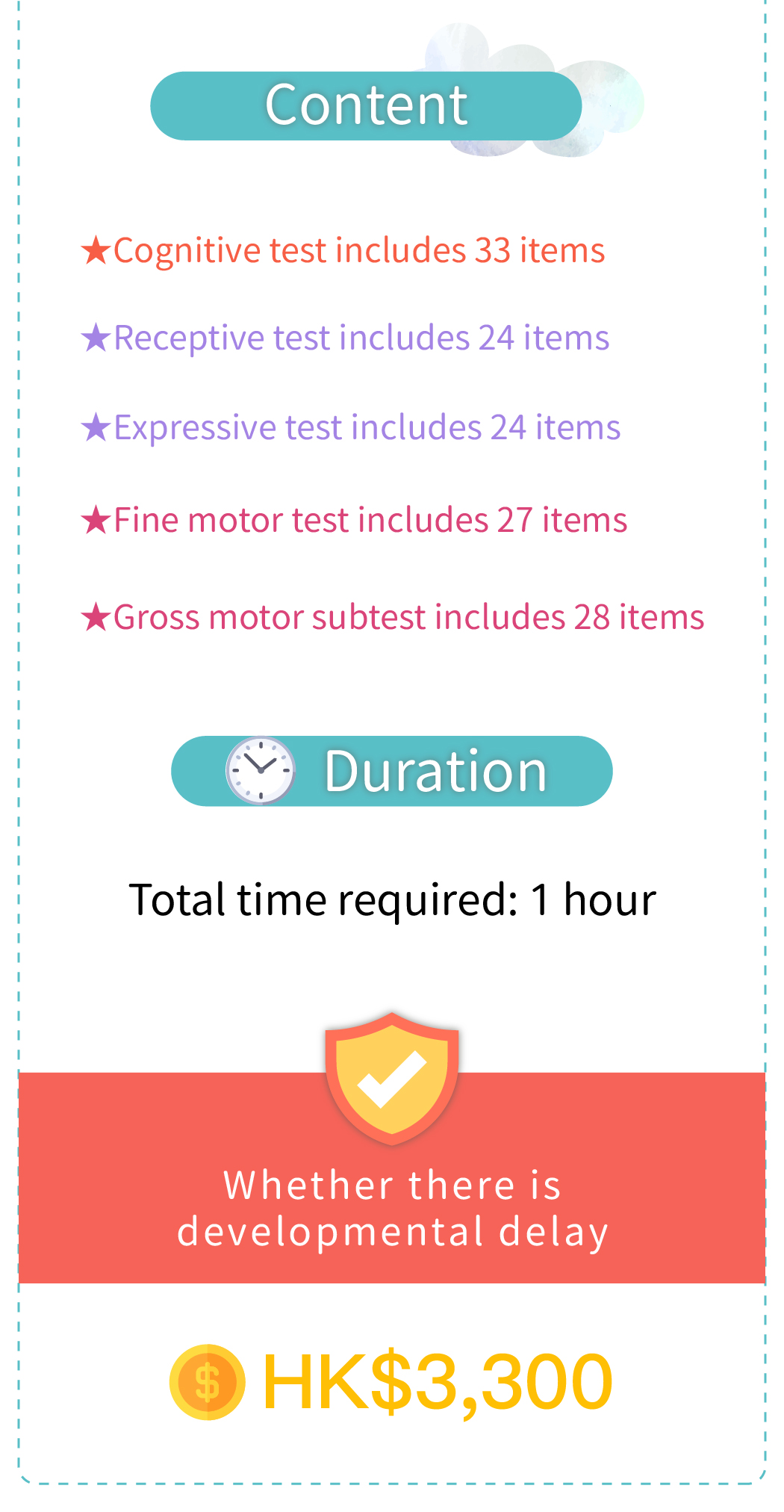
1. Pre-assessment parent interview
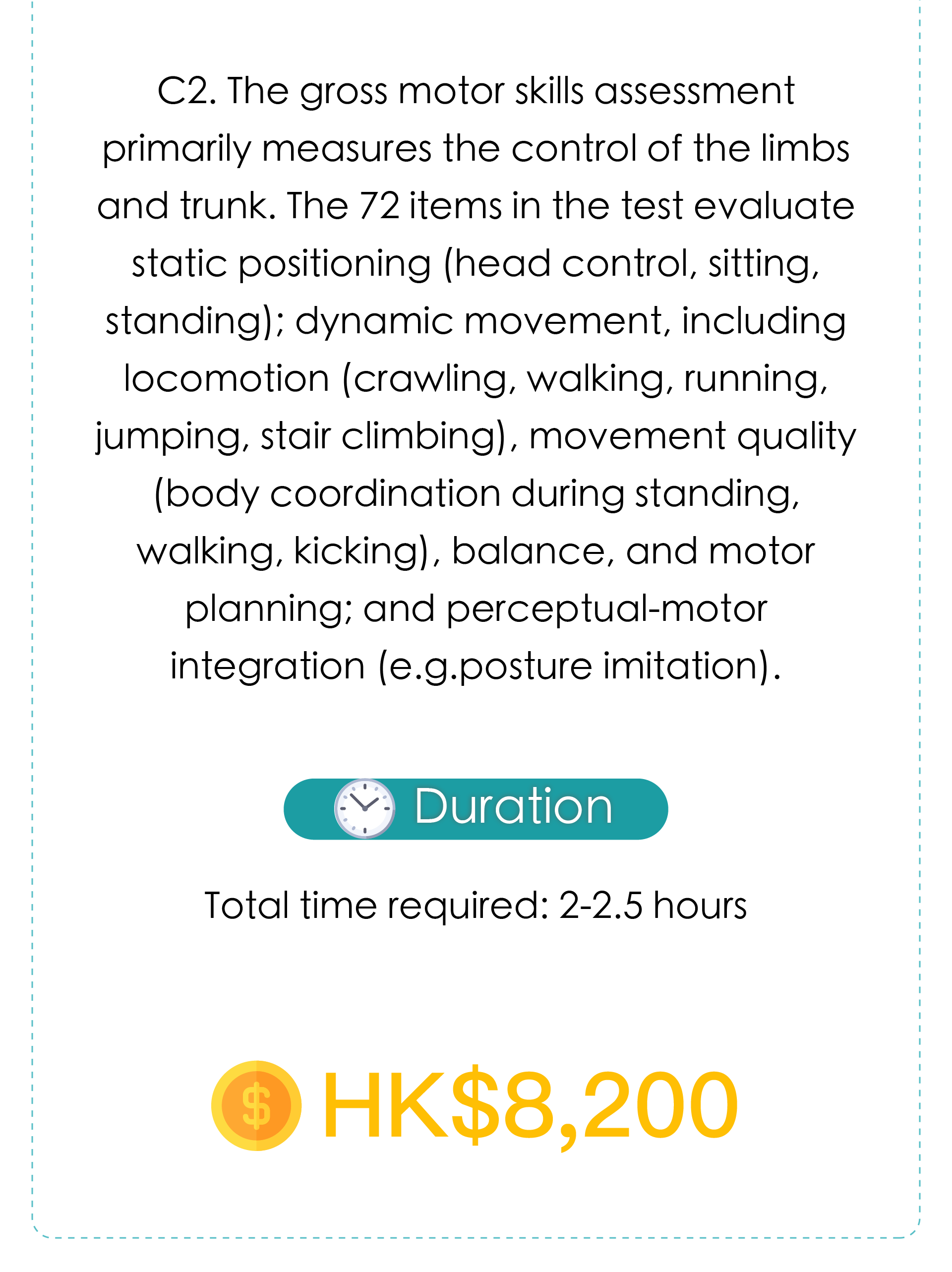
2.Developemental delay assessment by Pediatrician
3. Asssessment report (English)
4. Referral to specialists for further training
_0-49.jpg)
-8.png)
_0-51-scaled.jpg)
_0-52.png)
1. Pre-assessment parent interview
2. Bayley assessment by Pediatrician
3. Asssessment report (English)
4. Referral to specialists for further training
_0-54.jpg)
_0-55-scaled.jpg)
_0-52.png)
1. Pre-assessment parent interview
2. Developemental delay assessment by Pediatrician
3. Asssessment report (English)
4. Referral to specialists for further training
-2_1-3.png)
-2_1-4.png)
_0-52.png)
1. Pre-assessment parent interview
2. Developemental delay assessment by Pediatrician
3. Asssessment report (English)
4. Referral to specialists for further training
-2_1-7.png)
-2_1-8.png)
-2_1-9.png)
-2_1-10.png)
-2_1-11.png)
_0-52.png)
1. Discuss with parents about the findings, and analyze the growth and ability of the child
2. Provide recommendation
3.Provide Written asssessment report
4. Referral to specialists for further training
-2_1-15.png)
-2_1-16.png)
-2_1-17.png)
-2_1-18.png)
-2_1-19.png)
-2_1-20.png)
-2_1-21.png)
Diagnosis
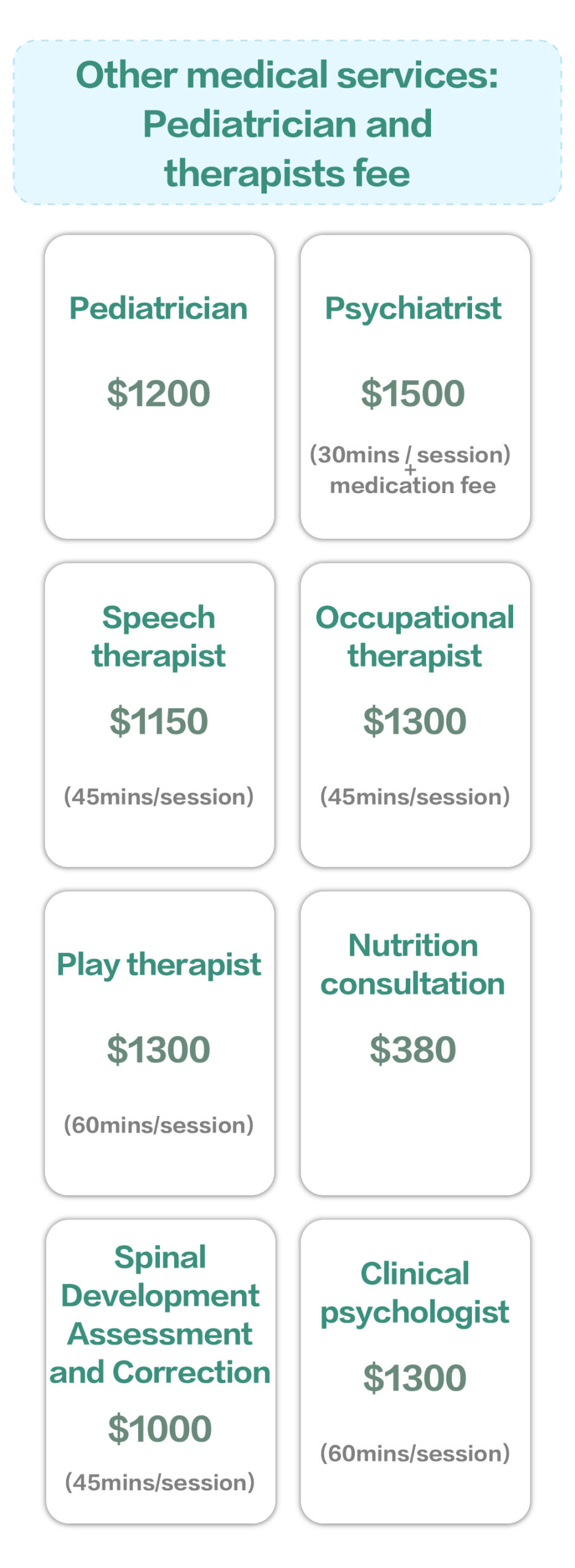
Speech therapy
Language development delay
Articulation disorder (incorrect pronunciation of words)
Vocal impairment, improper use of voice
Fluency disorder (commonly known as “stuttering”)
Social and communication disorders
Oral muscle activity and coordination disorders
Auditory speech disorder
Neurological communication disorder
Swallowing disorder rehabilitation
Difficulty swallowing
Eating behavior problems
Speech impediment
Dysarthria
Fluency disorder
Mispronunciation
Resonance problem
Cleft lip and palate, hearing impairment, trachea
Ostomy-related speech disorders
Language barrier
Aphasia
Mutism
Voice disorder
Oral muscle dysfunction
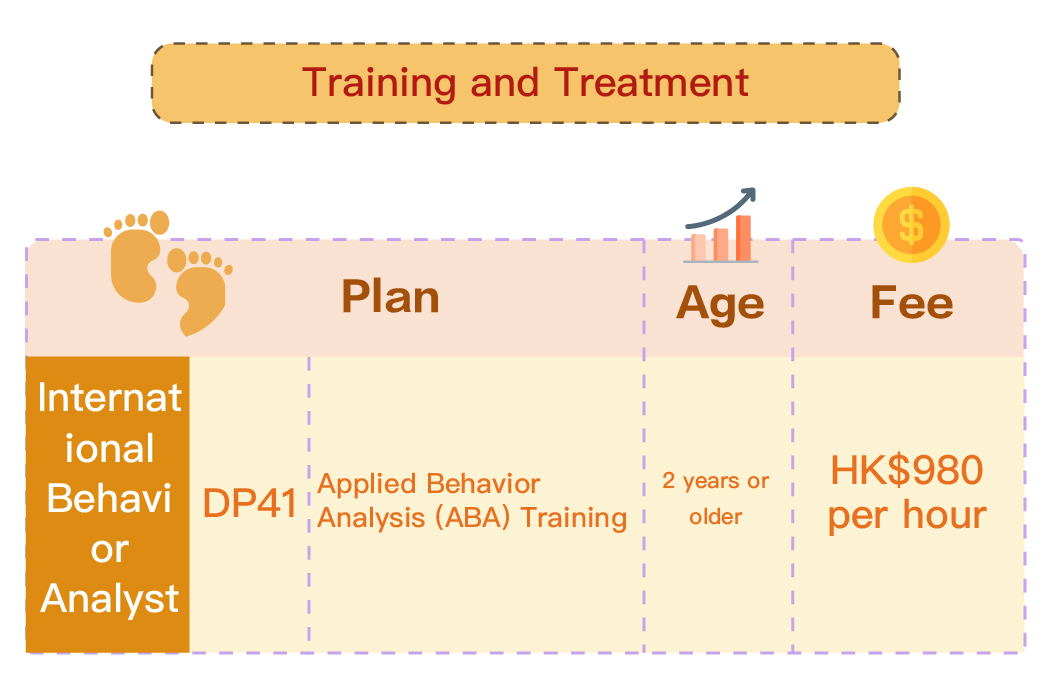
Oral muscle and eating assessment and training (including oral muscle, sensory, and treatment of eating behavior problems)
Occupational therapy
Assessment and training of activities of daily living, including skills such as self-care, home cooking, and use of community facilities
Baby sensory stimulation
Development assessment and training
Hand fine motor assessment and training
Writing assessment and training
Cognitive and Perceptual Assessment and Rehabilitation
Sensory integration therapy
Suggest and provide assistive devices to improve daily life
Functional and independent abilities
Sitting posture assessment, recommendations / configuration of related assistive devices
Neurorehabilitation
Clinical psychology
Assessment of cognitive and social-emotional functioning
Provide psychological assessment to help determine whether a child is suitable for individual medical procedures or surgeries
Assist with disease-related decision making and problem solving
Improve compliance with treatment regimen
Dealing with emotional distress and behavioral problems
Pain management
Caregiver Stress Management
Build resilience against disease
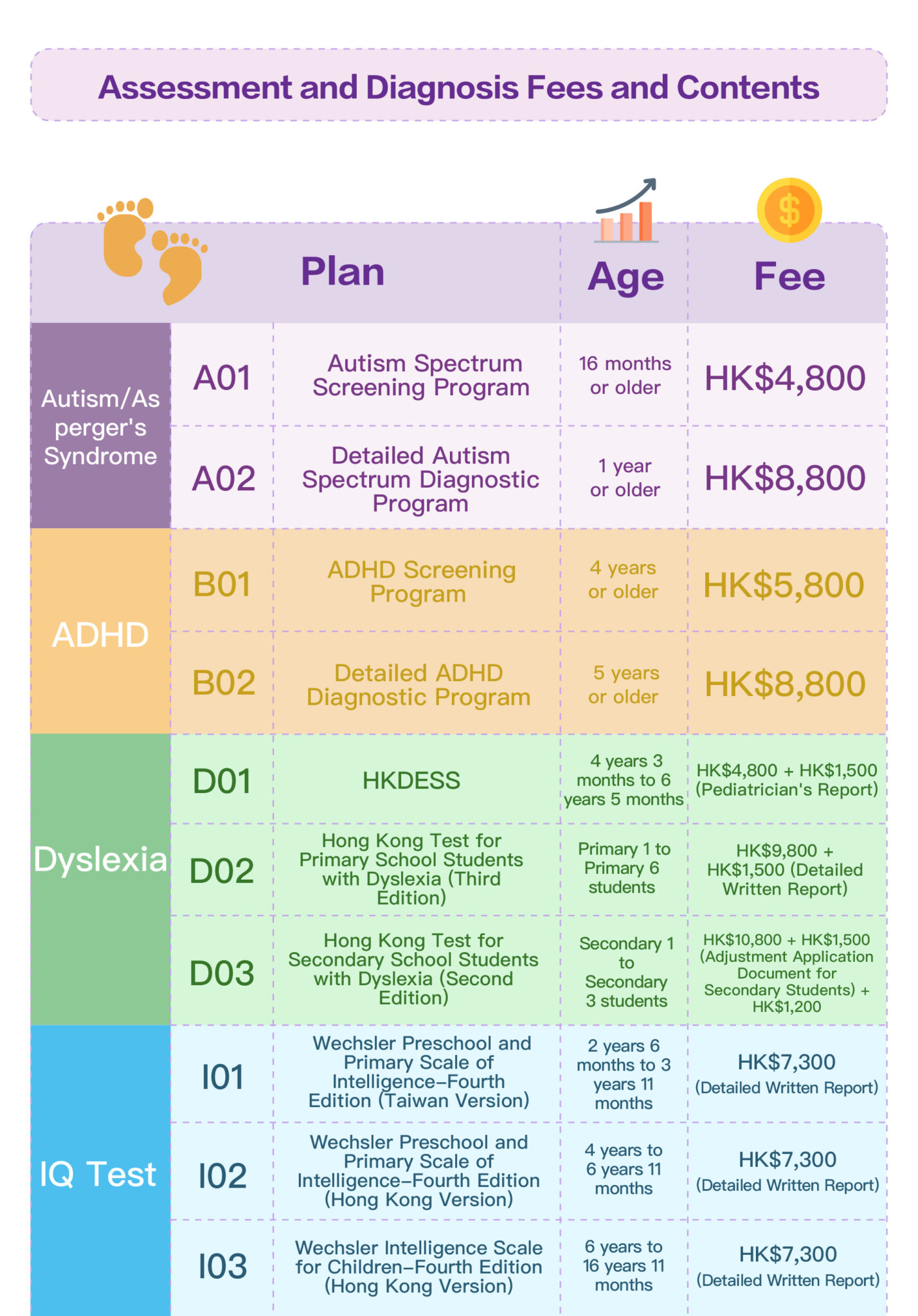
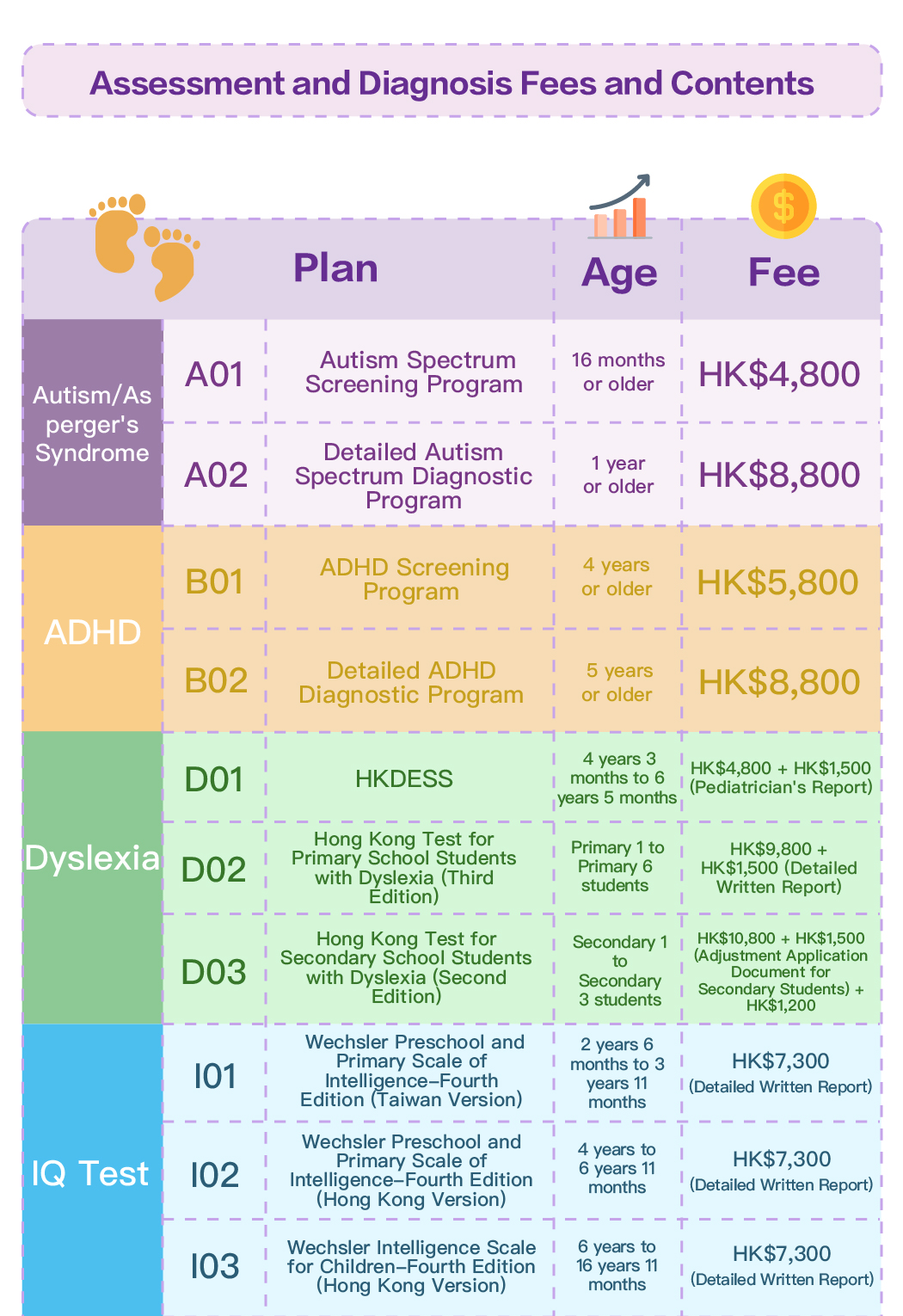
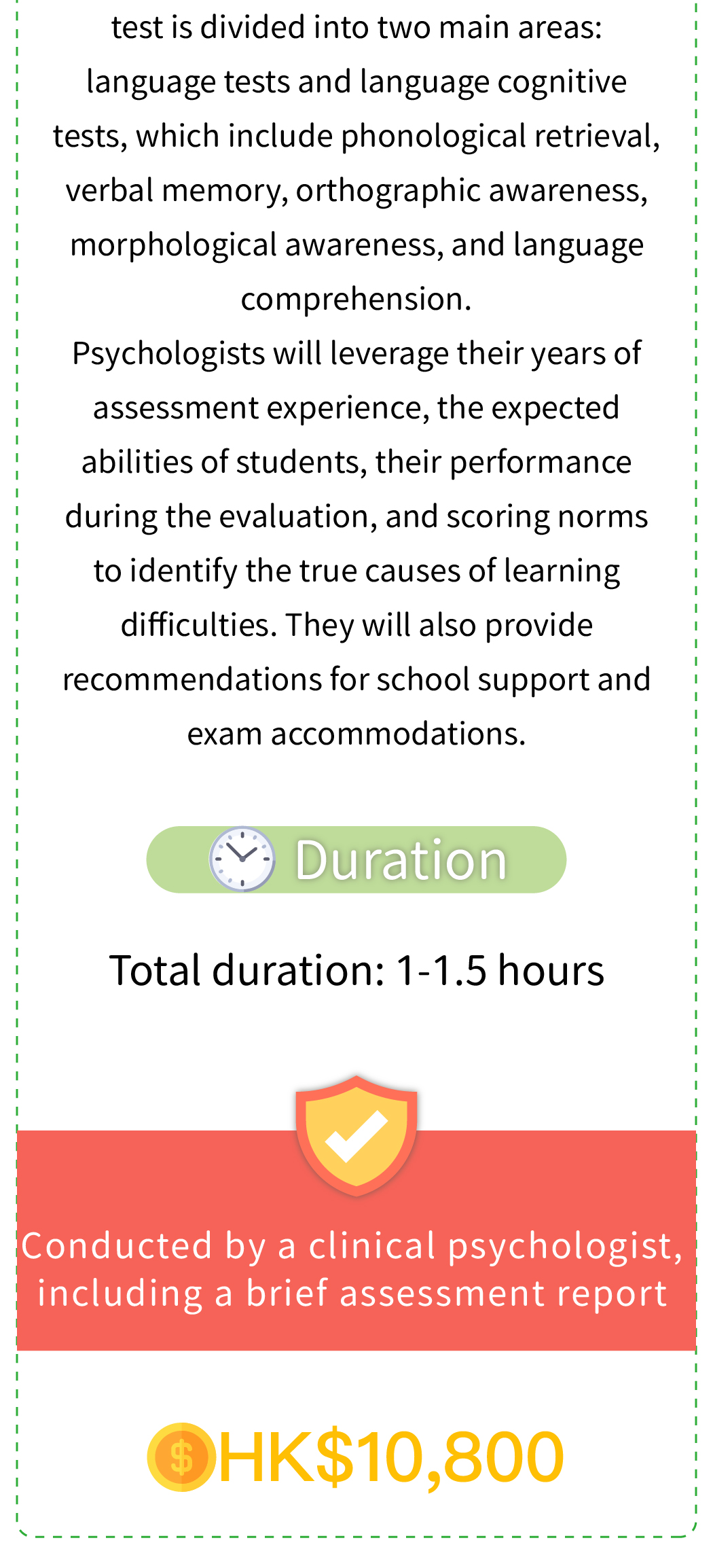
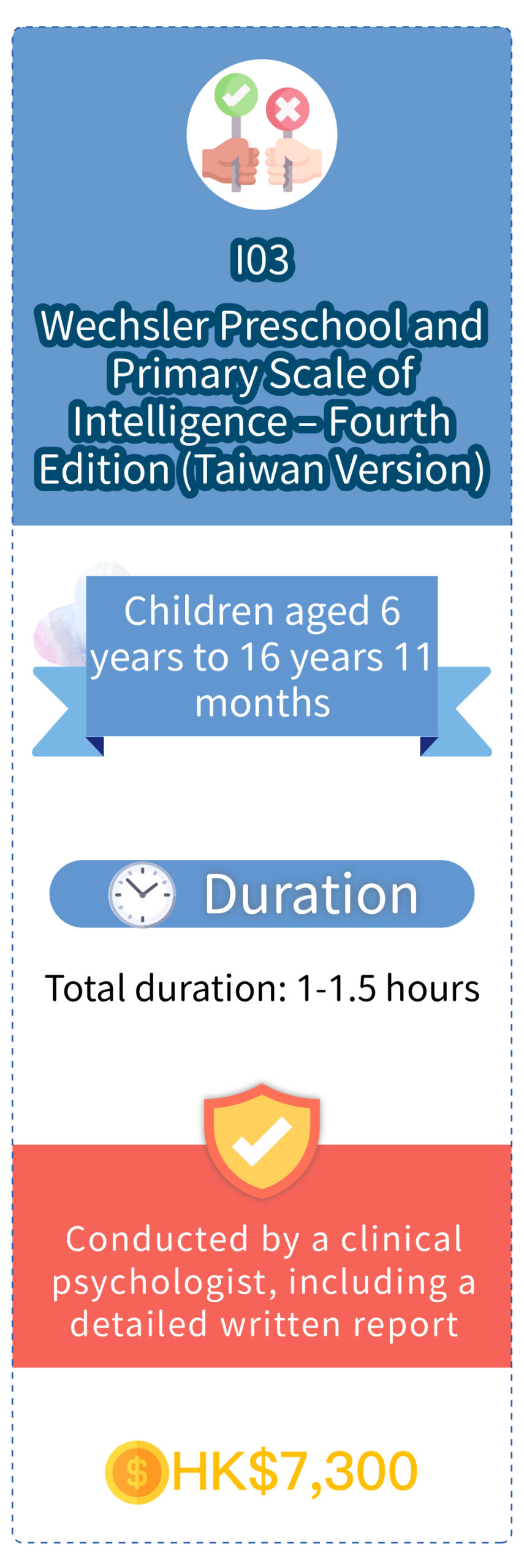
Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence™ – Fourth Edition (Hong Kong version) Hong Kong Dyslexia Test for Cantonese Primary School Students (Third Edition) (only applicable to primary school students) or Hong Kong Dyslexia Test for Junior Secondary School Students (Second Edition) (only applicable to junior secondary school students)
_0-2-822x1024.png)
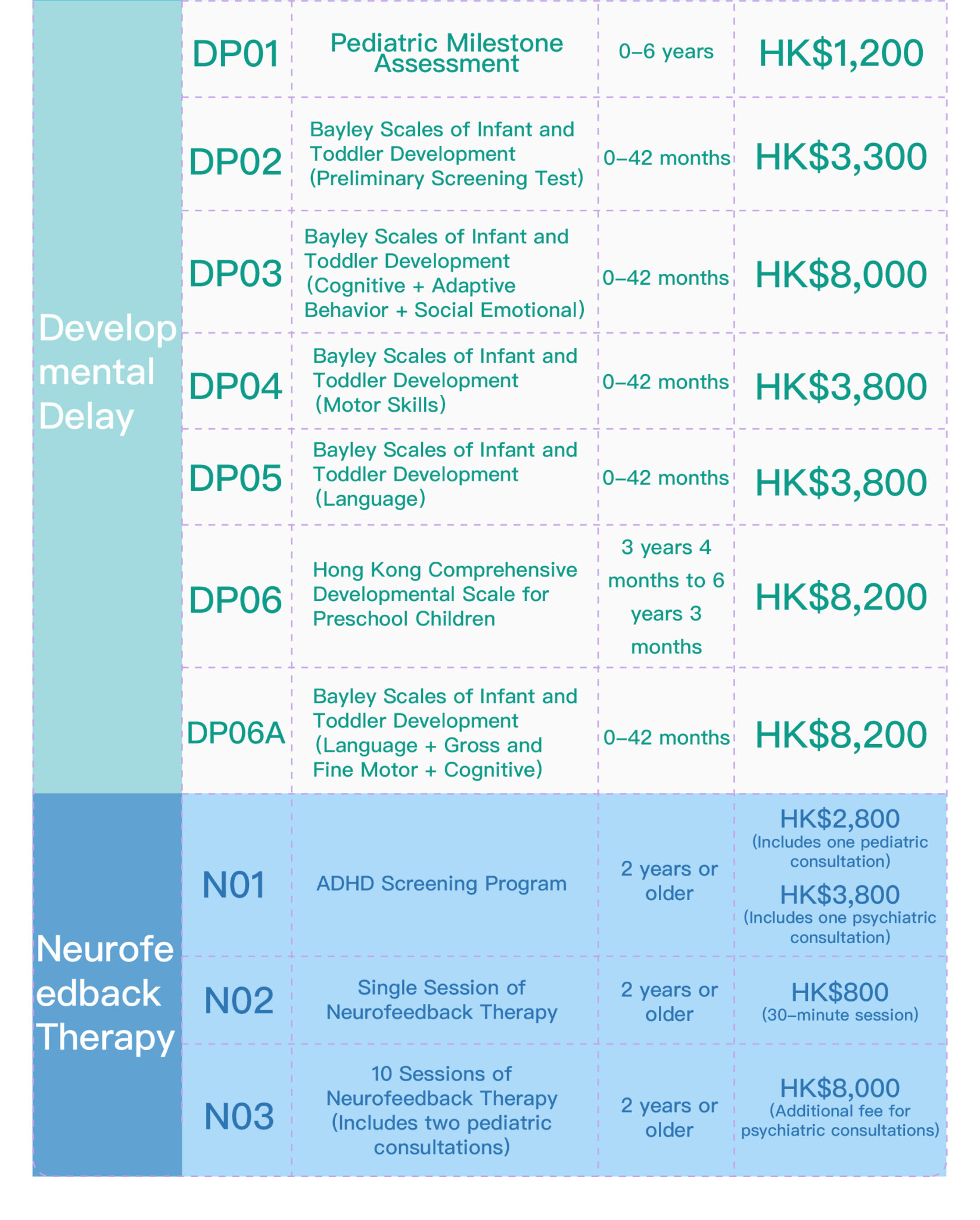



































































































_0-66.jpg)

-3_1-25.png)
.jpg)
